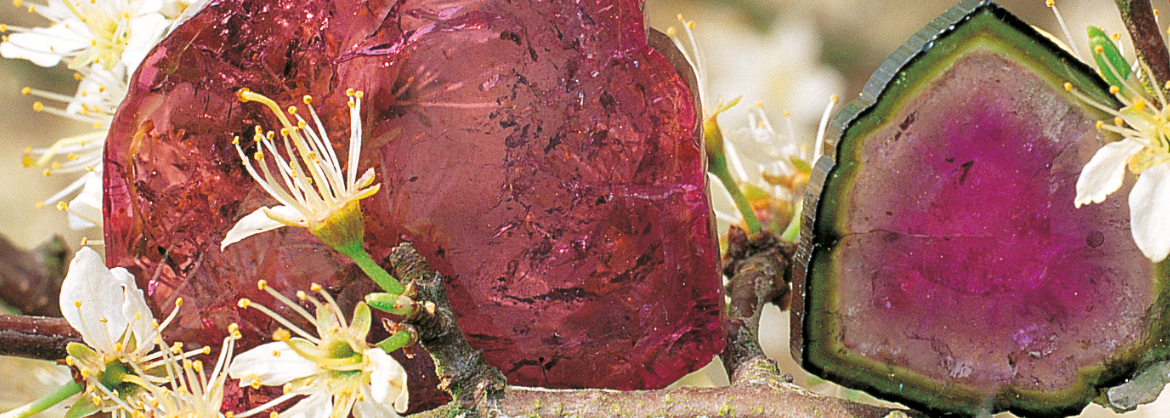

Tourmaline - Bearing, effect and application of a rainbow gemstone
The family of tourmalines can support us in various aspects: while the green tourmaline directs our gaze gratefully to the miracle of life and strengthens interest in our fellow human beings, the pink tourmaline helps us to be dedicate ourselves emphatically and full of devotion to our tasks. Black Tourmaline (black) promotes serenity and protects us from external influences. Thus, we can use the power of tourmaline according to our personal needs.
Mineralogical profile of Tourmaline
Chemical Forml (general formula tourmaline): Na,K,Li,Ca(Mg,Fe,Mn,Al)3(Al,Fe,Cr,Mn)6[(OH,F)4(BO3)3(Si6O18)]
Mineral class: complex boron minerals of ring silicates
Formation: primarily from acidic, boron-bearing magma, as a typical contact mineral by action on surrounding rock. Tourmaline may be primary-liquid magmatic, -pegmatitic-pneumatolytic, or -hydrothermal. The variety of Tourmaline depends on the nature of the rock and magma and its contact.
Transparency, luster: transparent to translucent; vitreous
Crystal system: trigonal
Mohs hardness: 7 - 7.5
Cleavability, fracture: None; small-muscle to brittle
Appearance: Tourmaline forms crystals with a triangular cross-section, with the side faces of prismatic crystals curving outward and typically showing distinct longitudinal striations. Long prismatic crystals are most commonly found with trihedral tips, smooth end faces, or irregular fibrous terminations; needle-like habit is referred to as tourmaline rods.
Localities: Tourmaline occurs almost worldwide, with 64 countries providing known collector material. The important group of liddicoatites comes exclusively from Madagascar. Significant sites for tourmalines are in Brazil, including the Paraiba district, home of the rare and sought-after Paraiba tourmaline. Another significant deposit was discovered in Nigeria in 1998.
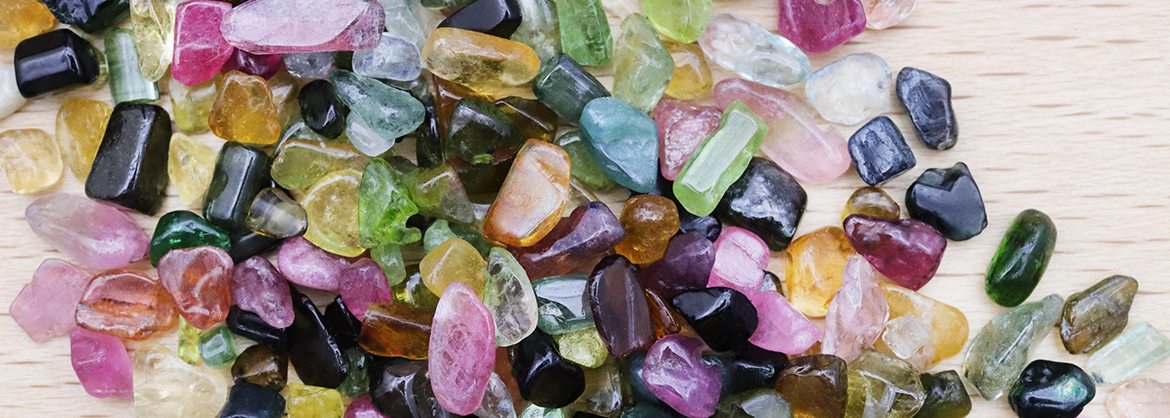

Varieties and colors of Tourmaline
The numerous varieties of the tourmaline group can be distinguished according to their chemical composition. Currently, 12 differentTourmalines are usually differentiated:
Buergerite - brown sodium-aluminum-iron Tourmaline
Chromdravite - green sodium-magnesium-chromium Tourmaline
Dravite - mostly brown sodium-magnesium-aluminum Tourmaline
Elbaite - multicolored lithium-sodium-aluminum-.Tourmaline
Feruvite - black calcium iron aluminum tourmaline
Foite - dark indigo blue iron aluminumTourmaline
Liddicoatite - multicolored lithium-calcium-aluminum tourmaline from Madagascar
Olenite - pale pink sodium-aluminum tourmaline, named after its locality on the Olenek River in Siberia
Povondrait - black sodium iron tourmaline
Silver - black sodium iron aluminum tourmaline
Tsilaisite - dark yellow sodium manganese-.Aluminum tourmaline
Uvite - mostly brown calcium-magnesium-aluminum tourmaline
Commercial names of Tourmaline
More common than the above mineralogical names are the trade names based on color, regardless of chemical composition:
Achroite (Greek. "the colorless") - clear, colorless Tourmaline
Indigolite (Greek "blue stone") - blue to indigo Tourmaline
Rubellite (lat. rubellos "reddish") - pink to red Tourmaline
Apyrites (Greek. a-pyrites "without fire") - violet Tourmaline
Tourmaline (black) - black Tourmaline
Verdelite (lat. viridis "green") - green tourmaline
Tourmalines exist in all colors of the rainbow and many other shades. In a crystal also color combinations can occur. Specialities include watermelon tourmaline with a red core and green rim, and moor's head tourmaline, a colored crystal with a black tip. Most tourmaline varieties are available only as expensive collectibles, i.e. as a crystal or specimen, or as a polished gemstone.
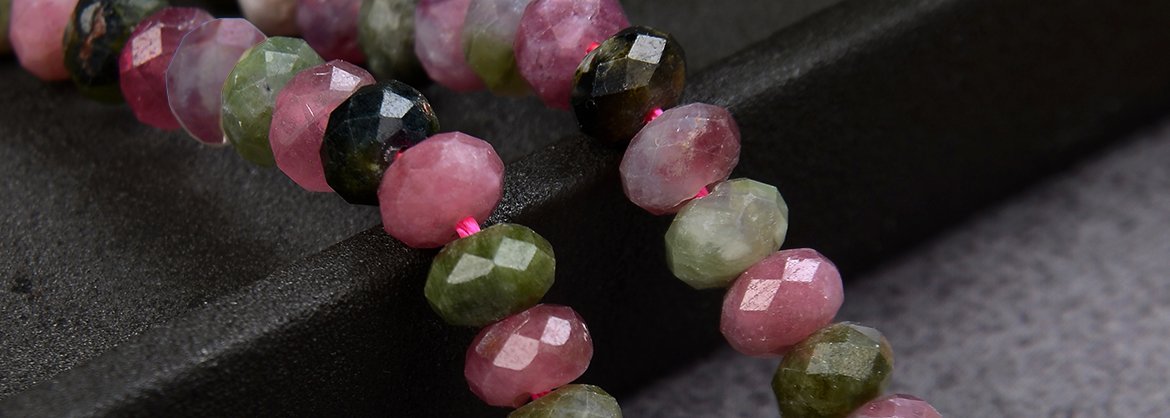

Origin of the name Tourmaline and synonyms
In Europe, the term "tourmaline" has been in use since the beginning of the 18th century. The name is derived from "thuramali" or "thoramalli", the Sinhala word for "stone of mixed colors".
Tourmaline became known in Europe through the extensive natural collection of the physician and botanist Paul Hermann, who worked as a doctor for the Dutch East India Company in Sri Lanka (Ceylon) in the 1670s.
Old synonyms for tourmaline in general are ash trekker, ash puller (due to electrical attraction), mountain flax (fibrous), iochroite, kalbaite, toramalli, trip as well as zeuxite. There are a variety of synonyms and trade names for the numerous different colored tourmalines. For example, emeralite and cromolite are other names for green tourmaline, light yellow tourmaline is also called canary tourmaline, and siberite is another name for purple tourmaline.
Usage of Tourmaline
Tourmalines are popular jewelry and therapy stones. For gemstone cutters, tourmaline can be very challenging due to internal stress in the crystals and because of its characteristic pleochroism. The strong pleochroism (colors and their intensity change when the stone is viewed from different angles) occurs because of birefringence. With the exception of Tourmaline (black), the members of the Tourmaline family belong to the higher price ranges. Top prices are achieved by the Paraiba Tourmalines thanks to their bright colors of sapphire blue, emerald green, purple, turquoise and pink.
Famous Tourmaline collections and Tourmalines
One of the world's most famous collections of Tourmaline slices can be found in the
Crystal Museum Riedenburg (Altmühltal, Lower Bavaria). There, more than 800 tourmalines can be marveled at - particularly fascinating here are tourmaline discs illuminated from behind, the "
crystallized rainbow".
The tourmaline has also made its way into the world of sports as early as 1949, as the rim of the German championship cup, which is awarded as a challenge cup for winning the German championship, has 21 green tourmalines set into it.
Historical aspects of Tourmlaine
The colorful Tourmalines fascinate and accompany people since before the time before the birth of Christ. The presumably first description of the gemstone is found in the work "De lapidibus" of the Greek philosopher and naturalist Theophrastos of Eresos (371 - 287 BC). Also in the well-known "Naturalis historia" of Pliny the Elder is reported about 77 AD about Tourmaline.
Tourmaline was often equated or confused with other gemstones for lack of mineralogical knowledge and gemmological examination methods. Thus, for example, the Portuguese believed in the 16th Jhdt., they had on the Brazilian gemstone fields of Minas Gerais. Three hundred years later, science caught up with this mistake, and the "Brazilian Emerald" was correctly identified as Green Tourmaline. Tourmalines were the favorite gemstones of our culture. and gemstones of the Biedermeier.
Applications of tourmaline in gemstone healing
Because of its good electrical conductivity and its richness in minerals, tourmaline is generally a dynamic, uplifting and invigorating therapeutic stone. It helps to unite spirit, soul, mind and body into a harmonious whole. The individual varieties of tourmaline show many special properties depending on their color and composition:
Blue (Indigolite)
Faithfulness and ethics; dissolves negativity and blockages; makes open, tolerant, promotes love of truth and a sense of responsibility
Brown (Dravite)
Sense of community; promotes helpfulness and social commitment; brings pragmatic creativity and manual dexterity.
Yellow
Happiness; promotes a happy, contented life and confidence in one's abilities; strengthens memory, enterprise, and positive worldview.
Green (Verdelite)
Thankfulness; helps to see the wonders of life; promotes interest in fellow human beings and the environment.
Paraiba Tourmaline
Love, beauty; enables experiencing the all-encompassing love for the world and all beings, brings deep dreams.
Polychrome
Wholeness; helps to unite spirit, soul, mind and body into harmonious unity; stimulates imagination and dreams; helps to recognize and control developments.
Red (Rubellite)
Lively; makes sociable, lively, promotes pleasure in sexuality; helps to devote oneself actively, emphatically and with dedication to a cause.
Violet (apyrite, siberite)
Wisdom; promotes deep peace of mind and helps to see other people and the world "whole"; helps to find the best ways to solve problems.
Watermelon Tourmaline
Understanding; promotes love, friendship and security, relieves anxiety and negative thoughts; helps to clearly express one's intention
Because, with the exception of Tourmaline (black), Tourmaline crystals are usually very small, the gemstone's energy often comes into play as a bracelet, necklace or other piece of jewelry.
Chakra and astrological aspects of Tourmaline
The color varieties of tourmalines determine the assignment to the chakras. Red tourmalines for the root chakra, orange for the sexual chakra, yellow for the solar plexus chakra, green and roas for the heart chakra, light blue for the throat chakra, dark blue ones for the brow chakra, and purple and white ones for the crown chakra.
American author Melody made an astrological assignment of the different varieties of tourmaline:
Colorless Achroite: Aquarius; yellow Tsilasite: Leo; light pink elbaite: Libra; pink rubellite: Sagittarius, Scorpio; blue indigolite: Libra, Taurus; brown dravite: Aries; green verdelite: Capricorn; Tourmaline (Watermelon): Virgo, Gemini



